Top 5 Casino Trực Tuyến, Uy Tín Hàng Đầu Tại Việt Nam 2025
Việc lựa chọn một nhà cái uy tín là điều quan trọng đối với người chơi cá cược trực tuyến tại Việt Nam. Với thị trường sôi động, không phải nền tảng nào cũng đảm bảo an toàn, minh bạch và hỗ trợ rút tiền nhanh chóng.
Top 5 Casino Trực Tuyến Hợp Pháp, An Toàn Tại Việt Nam 2025
| 1 |  | M88 Casino | M88 LINK | 🎉 188% khuyến mãi chào đón tại casino, nhận tối đa 3,888 VNĐ + vòng quay miễn phí. 🏆 125% khuyến mãi chào đón thể thao, nhận tối đa 4,288 VNĐ + hoàn tiền lên tới 60%. 💰 Hoàn tiền không giới hạn tại slot, bắn cá, thể thao, casino, keno… 🎯 Khuyến mãi nạp tiền lần 2 và 3 tại keno và xổ số, cược miễn phí 188 VNĐ. Yêu cầu: 20x vòng cược |
| 2 |  | FUN88 Casino | FUN88 LINK | 🎰 Thưởng 100% đăng ký tại trò chơi, casino, tối đa 2 triệu đồng. 🏅 Thưởng 100% đăng ký tại thể thao, esports, tối đa 6 triệu đồng. 🎲 Bảo hiểm 100% cược chung cuộc lên đến 10 triệu đồng. 💎 Giải độc đắc đôi 8 baccarat, trúng thưởng triệu đô. Yêu cầu: 18x vòng cược |
| 3 |  | 12Play Casino | 12Play LINK | 🎉 Thưởng ngay 100% cho thành viên mới. 💳 Xác nhận tài khoản, nhận ngay 40k. 💸 Hoàn trả live casino và cược thể thao không giới hạn từ 0,5% – 1%. 🎯 Thắng cược miễn phí lên đến 3,888,888 VNĐ. Yêu cầu: 25x vòng cược |
| 4 |  | We88 Casino | We88 LINK | 🎰 50% thưởng chào mừng tại sòng bài lên đến 2 triệu. 🏅 100% thưởng chào mừng tại thể thao lên đến 2 triệu. 💸 10% hoàn trả nạp tiền không giới hạn. 💵 Thưởng ngay 100k sau khi xác nhận tài khoản. Yêu cầu: 15x vòng cược |
| 5 |  | W88 Casino | W88 LINK | 🎯 Thưởng 100% lên đến 6150k tại thể thao, slot và bắn cá. 💰 Thưởng ngay 50 VNĐ cho khoản tiền gửi đầu tiên. 🎉 Tặng 18 vòng quay miễn phí cho giao dịch gửi tiền lần đầu. 🌟 Gửi tiền ngày vàng, thưởng nóng liền tay. Yêu cầu: 15x vòng cược |
Đánh Giá Chi Tiết Các Casino Trực Tuyến Tại Việt Nam
Để giúp người chơi có cái nhìn tổng quan và lựa chọn phù hợp, chúng tôi sẽ đánh giá chi tiết từng nhà cái dựa trên các tiêu chí như giấy phép hoạt động, chất lượng dịch vụ, ưu đãi và trải nghiệm người dùng.
M88 – Nhà Cái Cá Cược Uy Tín Với Hàng Ngàn Trò Chơi Hấp Dẫn
M88 (Mansion88) là thương hiệu cá cược nổi bật với nhiều năm kinh nghiệm trên thị trường châu Á. Nhà cái được cấp phép bởi chính phủ Vanuatu, mang đến đa dạng sản phẩm như cá cược thể thao, sòng bài trực tuyến, quay hũ jackpot và E-sports. Người chơi có thể tận hưởng trải nghiệm cá cược an toàn, minh bạch với tỷ lệ cược cao và nhiều khuyến mãi hấp dẫn, phải kể đến là 125% thưởng chào mừng lên đến 4288 VND cùng với hoàn tiền đến 60%.
| Tên công ty | Mountain Breeze Limited |
| Địa chỉ | Vanuatu |
| Giấy phép | Chính phủ Vanuatu |
| Chương trình VIP | Có |
| Ứng dụng | Có |
| Phí | Không |
Ưu điểm:
- Thương hiệu cá cược có uy tín lâu năm tại thị trường Việt Nam
- Đa dạng trò chơi, hợp tác với nhiều nhà phát hành lớn
- Cung cấp cá cược thể thao với tỷ lệ cược tốt
- Hệ thống bảo mật tiên tiến, đảm bảo an toàn cho người chơi
- Nhiều chương trình thưởng hấp dẫn cho thành viên mới và VIP
Nhược điểm:
- Một số chương trình khuyến mãi có điều kiện khá cao
Fun88 – Cá Cược Trực Tuyến An Toàn, Nhận Thưởng Liền Tay
Fun88 – Cá Cược Trực Tuyến An Toàn, Nhận Thưởng Liền Tay
Fun88 là một trong những nhà cái hàng đầu châu Á, được cấp phép hoạt động bởi Curaçao. Nhà cái này cung cấp đa dạng trò chơi cá cược, từ thể thao, casino trực tuyến đến quay hũ jackpot. Fun88 cũng là đối tác tài trợ chính thức của nhiều câu lạc bộ bóng đá danh tiếng, khẳng định vị thế trong ngành.
| Tên công ty | Omega Sports Solutions N.V |
| Địa chỉ | Curaçao |
| Giấy phép | Curaçao Gaming |
| Chương trình VIP | Có |
| Ứng dụng | Có |
| Phí | Không |
Ưu điểm:
- Nhà cái có thương hiệu lớn, uy tín tại Việt Nam
- Giao diện website và ứng dụng thân thiện, dễ sử dụng
- Kho trò chơi đa dạng, hỗ trợ cược thể thao, casino, e-sports
- Nhiều chương trình ưu đãi, hoàn tiền hấp dẫn
- Hệ thống bảo mật mạnh mẽ, đảm bảo an toàn thông tin
Nhược điểm:
- Một số trò chơi có mức cược tối thiểu khá cao
12Play – Trải Nghiệm Cá Cược Đẳng Cấp Với Nhiều Ưu Đãi Độc Quyền

12Play là một trong những sòng bạc trực tuyến được yêu thích nhất tại châu Á, sở hữu giấy phép hoạt động hợp pháp từ Curacao. Nhà cái cung cấp nhiều sản phẩm hấp dẫn như cá cược thể thao, casino trực tuyến, quay hũ jackpot, bắn cá và xổ số. Đặc biệt, 12Play có chương trình VIP với ưu đãi cực lớn dành cho thành viên thân thiết.
| Tên công ty | 12Play Limited |
| Địa chỉ | Curacao |
| Giấy phép | Curaçao Gaming |
| Chương trình VIP | Có |
| Ứng dụng | Có |
| Phí | Không |
Ưu điểm:
- Thương hiệu cá cược có giấy phép, đảm bảo an toàn
- Giao diện website hiện đại, hỗ trợ trên nhiều nền tảng
- Sở hữu hệ thống trò chơi đa dạng với tỷ lệ hoàn trả cao
- Nhiều chương trình khuyến mãi hấp dẫn dành cho thành viên mới
- Hỗ trợ thanh toán linh hoạt, bao gồm cả tiền điện tử
Nhược điểm:
- Thời gian duyệt rút tiền có thể lâu hơn vào giờ cao điểm
WE88 – Sòng Bài Trực Tuyến Chất Lượng Cao, Khuyến Mãi Hấp Dẫn
WE88 là nền tảng cá cược trực tuyến nổi tiếng với kho trò chơi đa dạng và giao diện thân thiện với người dùng. Nhà cái này cung cấp trải nghiệm cá cược toàn diện với các sản phẩm như casino trực tuyến, thể thao, bắn cá, quay hũ và poker. Đặc biệt, WE88 thường xuyên có các chương trình khuyến mãi hấp dẫn dành cho tân thủ như thưởng nạp lần đầu với giá trị tối đa lên đến 2000 VND.
| Tên công ty | WE88 Holdings Ltd |
| Địa chỉ | Curacao |
| Giấy phép | Gaming Curacao |
| Chương trình VIP | Có |
| Ứng dụng | Có |
| Phí | Không |
Ưu điểm:
- Nhà cái có giấy phép hoạt động hợp pháp, đảm bảo uy tín
- Giao diện website và ứng dụng mobile tối ưu cho người chơi
- Hệ thống trò chơi phong phú, tỷ lệ hoàn trả cao
- Hỗ trợ nhiều phương thức thanh toán linh hoạt
- Dịch vụ CSKH chuyên nghiệp, phản hồi nhanh
Nhược điểm:
- Link truy cập có thể bị chặn ở một số khu vực
W88 – Nhà Cái Cá Cược Hàng Đầu Châu Á, Tặng Thưởng Hấp Dẫn
W88 là một trong những thương hiệu cá cược trực tuyến hàng đầu châu Á, được cấp phép hoạt động bởi First Cagayan (CEZA) và vận hành hợp pháp tại nhiều quốc gia. Nhà cái cung cấp hàng loạt sản phẩm giải trí như Casino, Thể Thao, Esports, Slot Game, Bắn Cá, với tỷ lệ trả thưởng minh bạch và công nghệ bảo mật cao. Đặc biệt, tân thủ có thể nhận ngay 6150K tiền cược miễn phí khi đăng ký tài khoản.
| Tên công ty | Marquee Holdings Ltd |
| Địa chỉ | First Cagayan, Philippines |
| Giấy phép | First Cagayan (CEZA) |
| Chương trình VIP | Có |
| Ứng dụng | Có |
| Phí | Không |
Ưu điểm:
- Thương hiệu cá cược uy tín, hoạt động lâu năm tại thị trường châu Á
- Giao diện website và ứng dụng di động trực quan, hỗ trợ Android, iOS
- Cung cấp đa dạng trò chơi, tỷ lệ cược hấp dẫn
- Nhiều chương trình khuyến mãi giá trị dành cho thành viên mới và VIP
- Hỗ trợ nhiều phương thức thanh toán, bao gồm tiền điện tử
Nhược điểm:
Một số đường link có thể bị chặn tại Việt Nam
Casino Trực Tuyến Là Gì?

Casino trực tuyến là nền tảng cá cược online hiện đại, cho phép người chơi tham gia các trò chơi hấp dẫn ngay trên website hoặc ứng dụng di động. Chỉ cần đăng ký tài khoản và nạp tiền, bạn có thể trải nghiệm hàng loạt trò chơi cá cược như: Game bài, Slot, Bắn cá, Xổ số, Đua ngựa, Đá gà, Cá cược thể thao, Cá cược Esports,… Nếu giành chiến thắng, bạn có thể rút tiền về tài khoản một cách nhanh chóng và an toàn.
Các Tiêu Chí Lựa Chọn Nhà Cái Casino Trực Tuyến Uy Tín
Khi tham gia cá cược trực tuyến, việc lựa chọn một nhà cái uy tín là điều vô cùng quan trọng. Một nhà cái đáng tin cậy sẽ giúp bạn có trải nghiệm cá cược công bằng, bảo mật thông tin cá nhân và đảm bảo quyền lợi khi thắng cược. Dưới đây là một số yếu tố quan trọng khi lựa chọn nhà cái:
Giấy Phép Hoạt Động Hợp Pháp
Các nhà cái uy tín như M88, Fun88, 12Play, WE88 và W88 đều có giấy phép hoạt động hợp pháp từ các tổ chức quản lý cờ bạc uy tín như PAGCOR, Isle of Man, Curacao eGaming, Malta Gambling,…. Điều này đảm bảo mọi hoạt động đều minh bạch và an toàn cho người chơi.
Giao Diện Website Và Ứng Dụng Di Động Hiện Đại
Một casino trực tuyến chất lượng phải có giao diện web thân thiện, hỗ trợ đa ngôn ngữ (bao gồm tiếng Việt) và chạy ổn định trên nhiều trình duyệt. Ngoài ra, ứng dụng mobile trên Android và iOS cũng phải nhẹ, mượt, bảo mật cao, hỗ trợ đầy đủ các tính năng cá cược.
Kho Game Cá Cược Đa Dạng
Tại M88, Fun88, 12Play, WE88 và W88, bạn có thể trải nghiệm nhiều trò chơi từ những nhà phát hành hàng đầu như Evolution, Microgaming, Playtech, Pragmatic Play, Spadegaming, CQ9, JILI, NetEnt, Red Tiger… Các trò chơi đều đảm bảo đồ họa đẹp, công bằng và không có gian lận.
Tỷ Lệ Thưởng Minh Bạch, Thanh Toán Nhanh Chóng
Những nhà cái uy tín luôn cung cấp tỷ lệ thưởng hấp dẫn, rõ ràng và không có phí ẩn. Các giao dịch thanh toán được xử lý nhanh chóng, đảm bảo quyền lợi cho người chơi.
Nhiều Chương Trình Khuyến Mãi Hấp Dẫn
M88, Fun88, 12Play, WE88 và W88 thường xuyên tung ra các ưu đãi như:
- Thưởng chào mừng cho thành viên mới.
- Hoàn trả cược hàng tuần.
- Thưởng nạp lại.
- Thưởng VIP với nhiều quyền lợi hấp dẫn.
Hỗ Trợ Giao Dịch Đa Dạng, Nhanh Chóng
Các nhà cái uy tín hỗ trợ nạp/rút tiền bằng ngân hàng nội địa, ví điện tử, thẻ tín dụng, tiền mã hóa (crypto). Tất cả giao dịch đều được xử lý nhanh, không mất phí và có hệ thống bảo mật cao, đảm bảo không bị rò rỉ thông tin cá nhân của người chơi.
Dịch Vụ Chăm Sóc Khách Hàng 24/7
M88, Fun88, 12Play, WE88 và W88 đều có đội ngũ hỗ trợ khách hàng chuyên nghiệp qua nhiều kênh như Live Chat, Email, Zalo, Telegram, Hotline. Tất cả đều hoạt động 24/7 để giải đáp mọi thắc mắc nhanh chóng.
Chính Sách Bảo Mật Cao Cấp
Bảo mật thông tin người chơi là ưu tiên hàng đầu. Các nhà cái sử dụng công nghệ mã hóa SSL 128-bit để bảo vệ dữ liệu, đồng thời áp dụng chính sách bảo mật nghiêm ngặt để đảm bảo quyền riêng tư của người chơi.
Nên Cá Cược Tại Casino Uy Tín Trực Tuyến Hay Truyền Thống?
Giữa casino trực tuyến và casino truyền thống, đâu mới là lựa chọn tối ưu cho người chơi? Hãy cùng M88, Fun88, 12Play, WE88 và W88 so sánh hai mô hình này để đưa ra quyết định chính xác nhất!
| Tiêu chí | Casino Trực Tuyến (M88, Fun88, 12Play, WE88 và W88) | Casino Truyền Thống |
| Sự tiện lợi | Cực kỳ tiện lợi, có thể chơi mọi lúc, mọi nơi trên điện thoại, máy tính, iPad chỉ cần có kết nối internet. | Phải di chuyển đến địa điểm casino, mất nhiều thời gian, chi phí đi lại. |
| Tính an toàn & bảo mật | Bảo mật danh tính tuyệt đối, không lo bị lộ thông tin cá nhân nhờ công nghệ SSL 128-bit. | Nguy cơ bị lộ danh tính cao do phải xuất hiện tại casino vật lý. |
| Kho trò chơi | Cực kỳ phong phú với hàng nghìn game, liên tục cập nhật: Slot, Game bài, Bắn cá, Xổ số, Đá gà, Cá cược thể thao, Esports… | Hạn chế về số lượng trò chơi do diện tích casino có giới hạn. |
| Tỷ lệ thưởng | Tỷ lệ thưởng cao, minh bạch, dễ thắng lớn. | Tỷ lệ thưởng thấp hơn do casino truyền thống có nhiều chi phí vận hành. |
| Khuyến mãi & ưu đãi | Nhiều khuyến mãi hấp dẫn như: Thưởng chào mừng, Hoàn trả cược, Thưởng VIP, Tặng Free Bet… | Không có khuyến mãi dành cho người chơi. |
| Tiền tệ cá cược | Hỗ trợ nhiều loại tiền tệ, bao gồm VNĐ, USD, Crypto (BTC, USDT…). | Chỉ hỗ trợ tiền mặt, không có tùy chọn tiền điện tử. |
| Mức tiền cược | Linh hoạt, chỉ từ vài nghìn đồng đến vài trăm triệu. | Mức cược cao, thường từ vài trăm nghìn đồng trở lên. |
Hướng Dẫn Cách Tham Gia Cá Cược Tại TOP Casino Trực Tuyến Uy Tín
Bạn có thể dễ dàng tham gia cá cược tại các casino trực tuyến uy tín như M88, Fun88, 12Play, WE88 và W88 chỉ với vài bước đơn giản. Dưới đây là hướng dẫn chi tiết giúp bạn bắt đầu trải nghiệm cá cược chuyên nghiệp ngay hôm nay!
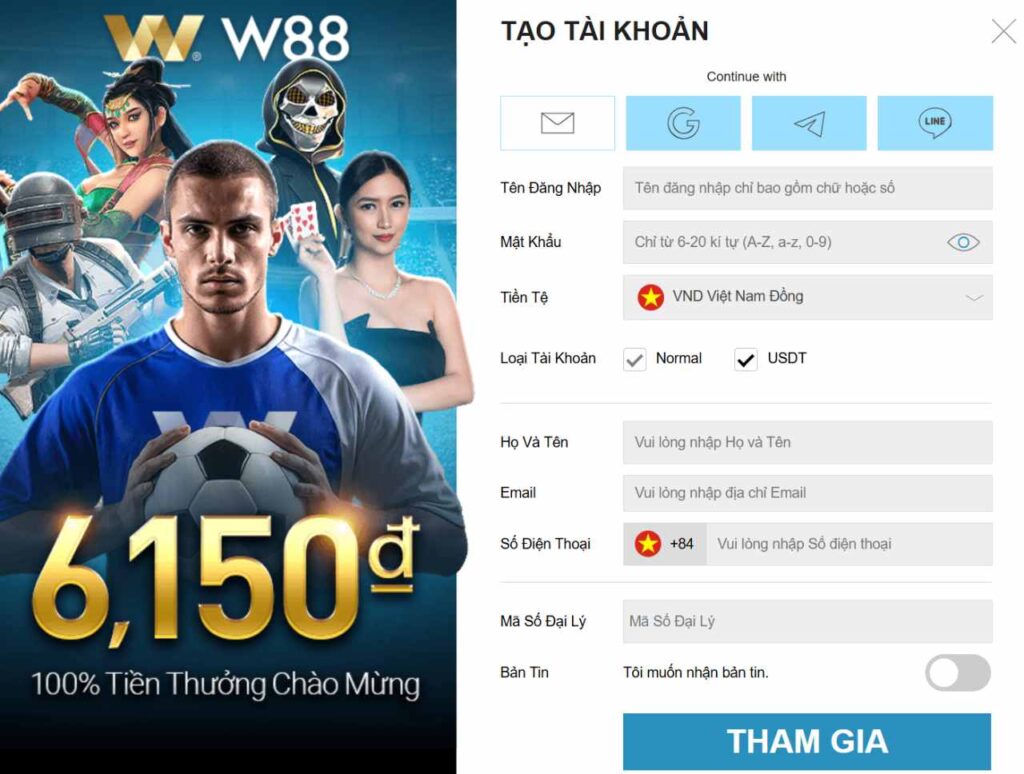
Bước 1: Đăng Ký Tài Khoản
- Truy cập trang web chính thức của M88, Fun88, 12Play, WE88 và W88 bằng trình duyệt trên máy tính, điện thoại hoặc iPad.
- Nhấn vào nút “Đăng ký” hoặc “Tham gia ngay”.
- Điền thông tin cá nhân vào biểu mẫu đăng ký.
- Nhấn nút “Tham gia” để tạo tài khoản cá cược thành công.
Lưu ý: Hãy nhập thông tin chính xác để thuận tiện cho việc xác minh và rút tiền sau này.
Bước 2: Đăng Nhập Và Nạp Tiền
- Đăng nhập vào tài khoản vừa tạo tại M88, Fun88, 12Play, WE88 hoặc W88.
- Nhấn vào mục “Nạp tiền” để tiến hành giao dịch.
- Chọn một trong các phương thức thanh toán được hỗ trợ: Chuyển khoản ngân hàng, Momo, ZaloPay, ViettelPay, Crypto (BTC, USDT)…
- Nhập số tiền cần nạp và điền thông tin vào biểu mẫu.
- Nhấn “Gửi đi” và đợi hệ thống xử lý trong vài phút.
Lưu ý: Các nhà cái này hỗ trợ nhiều loại tiền tệ, giao dịch an toàn, nhanh chóng và không mất phí ẩn.
Bước 3: Chọn Thể Loại Game Cá Cược
- Sau khi nạp tiền, bạn có thể chọn game cá cược yêu thích từ danh mục trò chơi đa dạng của nhà cái.
- Một số sảnh game phổ biến tại M88, Fun88, 12Play, WE88 và W88:
Casino Trực Tuyến: Baccarat, Roulette, Blackjack, Sicbo…
Slot Game: Nổ hũ đổi thưởng, Jackpot lũy tiến…
Cá Cược Thể Thao: Bóng đá, Esports, Tennis, Bóng rổ…
Bắn Cá, Xổ Số, Đá Gà…
Bước 4: Đặt Cược & Trải Nghiệm Game
- Chọn bàn cược phù hợp với số vốn của bạn (cược nhỏ, cược lớn).
- Đặt cược và theo dõi kết quả ngay trên màn hình.
- Nếu thắng, tiền thưởng sẽ được cộng vào tài khoản ngay lập tức.
Mẹo: Hãy tận dụng các chương trình khuyến mãi để nhận tiền thưởng khi chơi!
Câu Hỏi Thường Gặp Khi Cá Cược Tại M88, Fun88, 12Play, WE88 và W88
1. Có thể cá cược tại Casino trực tuyến bằng tiền Việt Nam không?
Có. Tất cả các nhà cái M88, Fun88, 12Play, WE88 và W88 đều hỗ trợ người chơi cá cược bằng tiền Việt Nam Đồng (VND). Ngoài ra, còn có nhiều loại tiền tệ khác như USD, THB, MYR, IDR…
Bạn có thể nạp và rút tiền nhanh chóng thông qua chuyển khoản ngân hàng, Momo, ZaloPay, ViettelPay, Crypto (BTC, USDT)…
2. Thành viên mới có thể nhận được khuyến mãi gì khi đăng ký?
Các nhà cái M88, Fun88, 12Play, WE88 và W88 luôn có chương trình khuyến mãi hấp dẫn dành cho thành viên mới, bao gồm:
Thưởng chào mừng 100% khi nạp tiền lần đầu.
Tặng cược miễn phí không cần nạp tiền.
Hoàn tiền VIP khi chơi Casino trực tuyến.
Thưởng nạp lại hàng tuần và khuyến mãi theo sự kiện.
Lưu ý: Mỗi nhà cái có chính sách ưu đãi khác nhau, hãy kiểm tra chi tiết trên trang web chính thức để không bỏ lỡ bất kỳ ưu đãi nào!
3. Có thể cá cược tại Casino online trên điện thoại không?
Có! Bạn hoàn toàn có thể chơi Casino trực tuyến ngay trên điện thoại theo 2 cách sau:
- Truy cập trực tiếp vào trang web chính thức của M88, Fun88, 12Play, WE88 hoặc W88 bằng trình duyệt trên điện thoại.
- Tải và cài đặt App Mobile của các nhà cái để có trải nghiệm chơi mượt mà hơn.
Ưu điểm khi chơi trên điện thoại:
Giao diện tối ưu, dễ sử dụng.
Cá cược mọi lúc, mọi nơi.
Hỗ trợ đầy đủ các tính năng như trên máy tính.
Kết Luận
M88, Fun88, 12Play, WE88 và W88 là những casino trực tuyến uy tín hỗ trợ cá cược bằng VND, có nhiều khuyến mãi hấp dẫn cho thành viên mới và cho phép chơi game trên mọi thiết bị. Tham gia ngay để tận hưởng trải nghiệm cá cược đỉnh cao cùng hàng loạt ưu đãi hấp dẫn!
